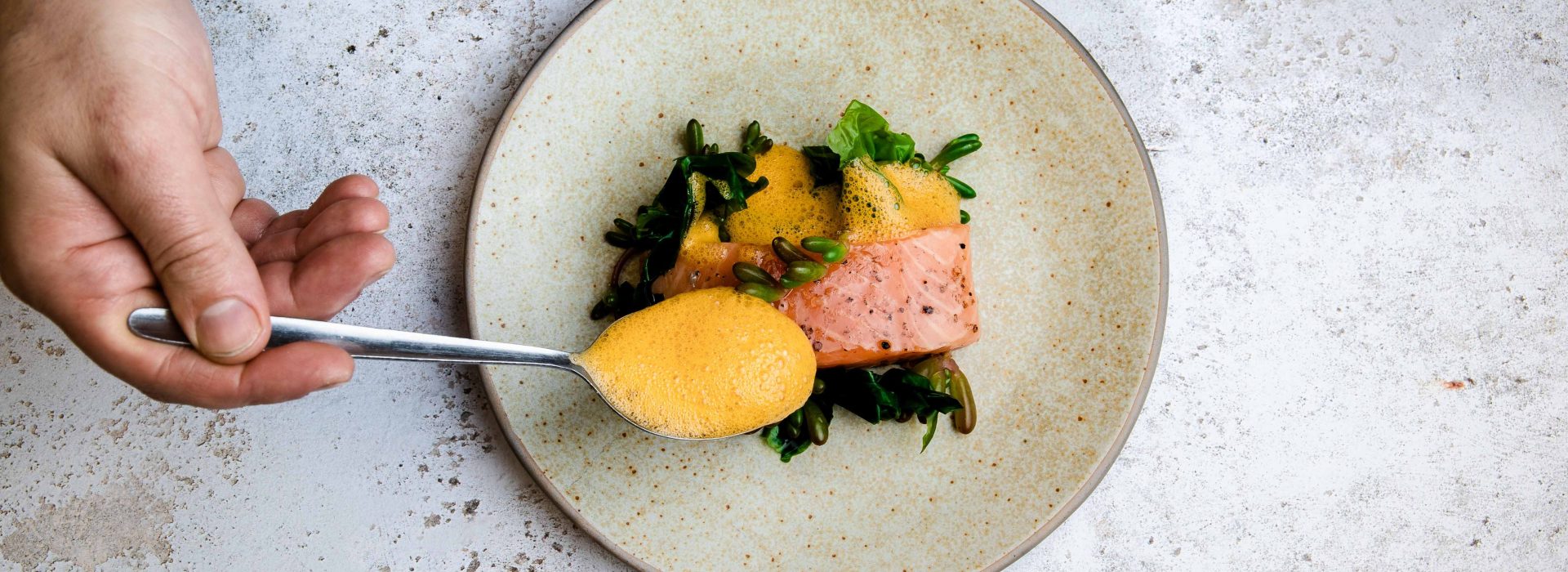Food, diets, and traditional cultural practices related to food are strong drivers of cultural identity. They provide communities with a sense of social integration, inclusiveness, peace, and stability. In many societies, eating together is the foundation of cultural continuity, associated with social exchange, and an affirmation and renewal of family, group, and community identity. The production, processing, trade, preparation, and consumption of food involve skills, knowledge, traditions, and natural resource management practices that bring people together. Many societies have found ways to produce and consume food in harmony with their environment, drawing on their knowledge and heritage as key resources to be preserved and passed onto future generations, for the benefit of better health, nutrition, food safety, prevention of food waste, care practices, natural resource management and social cohesion.
Transformation of Food Systems
Over the last century, food systems have undergone considerable transformation due to technological advances, the massive use of fossil fuels, migration, urbanization, and globalization. This transformation has brought important benefits in terms of increased food production, able to feed a growing world population. However, it has also produced negative impacts that pose risks to the sustainability of the planet and the existence of humanity: loss of cultural and ecological diversity; marginalization of large groups of family farmers, pastoralists, artisanal fisher-folks, and other rural populations; erosion of everyday culinary culture and people’s knowledge of food preparation; increased consumption of ultra-processed food, that is poor in fiber and micronutrients, but rich in caloric energy, additives, and anti-microbial substances, affecting the composition of the human microbiome; and rapid rise in obesity and associated non-communicable diseases (NCDs).

Photo by on Pexels
FAO and UNESCO Collaboration
The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) have collaborated on a study titled “Chefs as Agents of Change”. The study highlights the role of chefs in addressing the challenges of malnutrition, particularly obesity and diet-related NCDs, and the acceleration of the loss of cultural and ecological diversity. These initiatives however are inadequately reflected in sectoral policies on health, agriculture, or markets, which shape food systems. Government actions to address malnutrition challenges must include a focus on influencing consumer and private sector knowledge, attitudes and behaviours, which requires bringing the cultural dimensions of agriculture and food into development and sectoral policies.
The Role of Chefs
Chefs today are among the actors who shape public opinion and influence the general population, the private sector, and governments. In the last two decades, a growing number of Chefs de Cuisine have looked to traditional food systems, recovering the notion of food linked to the territory and local culture, and promoting a revision of culinary trends to offer delicious and healthy food. This growing trend considers that healthy diets rely on the quality of ingredients from their initial stage of production and values the role of local producers in supplying fresh, diverse, and safe food produced in a sustainable way.
Joint FAO-UNESCO Initiative
FAO and UNESCO, in collaboration with member states, have worked together towards recognizing the importance of the cultural dimensions of production systems and food. There is scope for greater cooperation between FAO, UNESCO, and chefs in addressing these challenges. The objectives of a joint FAO-UNESCO initiative would be to advocate for the value of culture in achieving sustainable food systems and healthy diets as well as for the importance of agriculture and food in shaping culture in different communities, underlining the importance of diversity.
Way Forward for FAO and UNESCO
Achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) requires greater coherence and collaboration between multiple stakeholders. A joint initiative between FAO and UNESCO on food and culture, involving chefs as agents of change, presents an important opportunity for joint advocacy work on the importance of culture and heritage in achieving healthy diets and sustainable agriculture. This can be done by building on the existing cooperation between UNESCO’s 1972 Convention concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage, the UNESCO Man and the Biosphere (MAB) Programme and World Network of Biosphere Reserves, the UNESCO Global Geoparks and FAO’s Globally Important Agricultural Heritage Systems (GIAHS) Programme.
The full study can be accessed through the following link: FAO and UNESCO Study
For more information about the organizations involved in this study, please visit their official websites:
- Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO)
- United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO)
[1] FAO and UNESCO. (2019). Chefs as Agents of Change. [online] Available at: https://www.fao.org/3/ca3715en/ca3715en.pdf [Accessed 3 Aug. 2023].